One of the things that has great potential to irritate is the denial of fundamental, proven scientific truths. A lot of confusion can come from the fact that a scientific theory is very different from the regular understanding of the word “theory”.
A scientific theory is a well-substantiated explanation of some aspect of the natural world that is acquired through the scientific method and repeatedly tested and confirmed, preferably using a written, pre-defined, protocol of observations and experiments. Scientific theories are the most reliable, rigorous, and comprehensive form of scientific knowledge.
Wikipedia
So, to cut through this confusion, here’s a MEME to show what evolution is:

First of all, I am not a scientist, but I do know how to read and how to think for myself. Also, when something matters to me, I will take the time to study it, to read about it, and to make myself at least a bit more familiar with it than I would have been if I had relied on my education alone. The sad fact is that education in my time (and even today) is not focused on teaching critical thinking but on memorising facts, which makes students more robots than educated citizens. But I digress.
So, how do scientists know that evolution really happened?

By Zephyris at the English language Wikipedia, CC BY-SA 3.0, Link
When you think about potential Evidence for evolution, you immediately think of FOSSILS. But, as we shall see, fossils are actually only extra, bonus, icing on the cake … however you wish to call it. The case for evolution would be air-tight without any fossil evidence whatsoever!!
How? Well, let’s see.
The first thing you should know is that there is not only Evidence, but GROUPS of Evidence, with TONS of examples in each group. So, what are these groups?
- Fossil evidence
- Evidence from physical similarities between species (anatomy)
- Evidence from biogeography – Geographical distribution of species
- Genetic evidence
- Natural selection directly observed
It is also worth noting that, for example, speciation is evident in the fossil record, which makes all groups interconnected and points to the same conclusion: Common Descent.
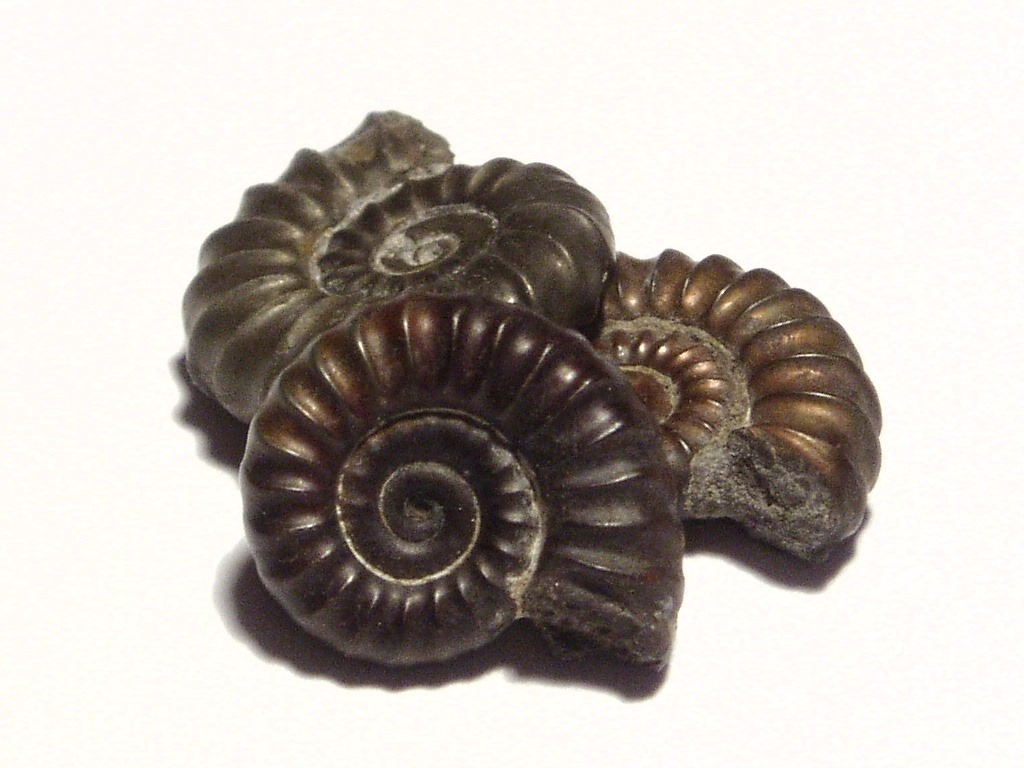
1. Fossil evidence
Not much needs to be said about fossil evidence. This is one type of Evidence everybody’s familiar with, more or less. Basically, it is possible to show how life evolved by arranging and displaying the fossils found in order.
This is possible because fossils are found in layers, and as layers are added on top of each other, the oldest fossils are found in the lowest layers, and the youngest fossils are in the highest layers of the rock.
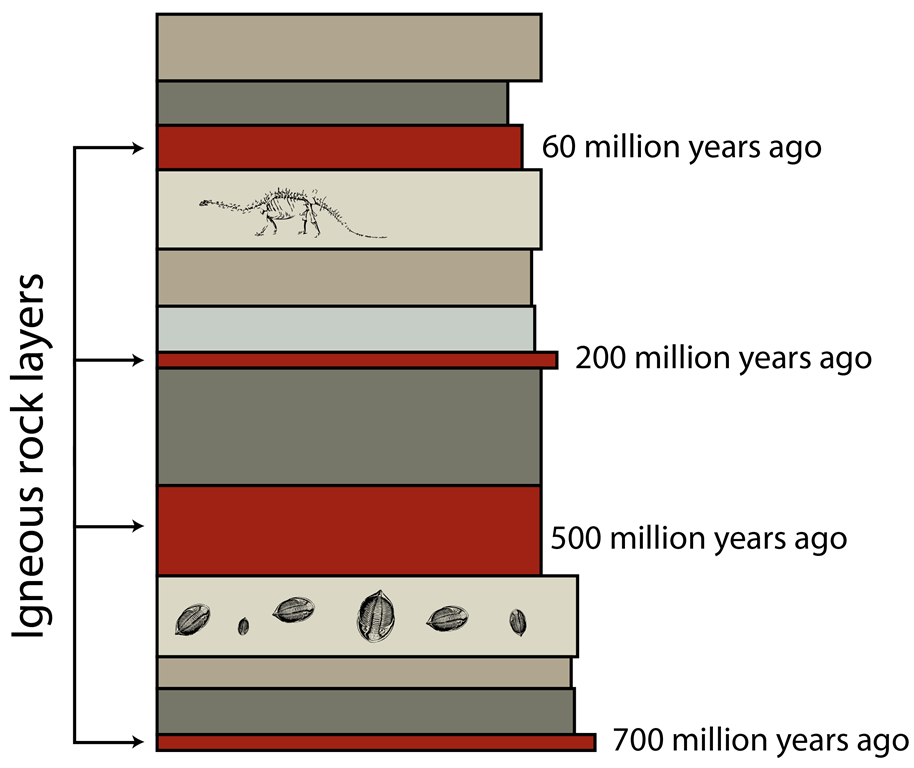
By Jillcurie (Own work) [CC BY-SA 3.0], via Wikimedia Commons
This also allowed scientists to see that the fossils which appeared earlier disappeared later.
In the past, scientists could only more or less estimate the age of these layers, but now this can be determined much more accurately using radiometric dating.
2. Evidence from anatomy
This group of Evidence is easily overlooked when thinking about evolution, yet it is very, very obvious when you are made aware of it.
When plants and animals are closely examined, both scientists and ordinary people can see that, although different species of plants and animals are distinct, they are really, really similar. This is easiest to see in flowers.
For example, the basic structure of all flowers consists of sepals, petals, stigma, style and ovary; yet the size, colour, number of parts and specific structure are different for each individual species. (Wikipedia)
Other topics frequently mentioned when discussing Evidence from anatomy include skeletons. When skeletons are examined, they are, of course, different, but also the same in a way, meaning they contain the same bones.
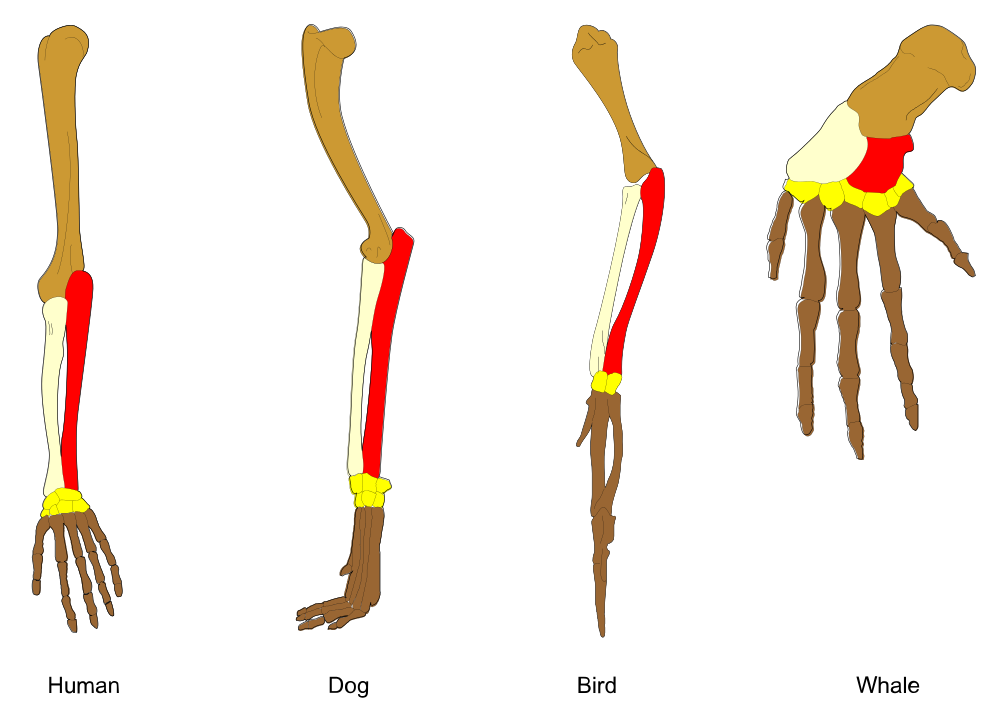
By Волков Владислав Петрович (Own work) [CC BY-SA 4.0], via Wikimedia Commons
Another beautiful example Richard Dawkins uses in the book “The Greatest Show On Earth: The Evidence For Evolution” is the bat skeleton, in which he points out the similarities between human hands and bat wings. A bat’s wing and a human hand are two versions of the same thing. He even mentions our and bats’ similarities to pterodactyl!
There are other forms of common traits in modern animals, and they all point to one thing: common descent and evolution over millions of years. Examples of this Evidence include remnants of eyes in animals that lost their sight through adaptations to the environment. Various insect mouths have the same structure … There are countless examples. This body of Evidence is supported by the previous body of proof—the fossils. See how it all fits together?
3. Evidence from the geographical distribution of species
Evolution is driven by mutation and natural selection. The most successful organisms are those that do NOT get eliminated – meaning they are optimal to survive and reproduce. This means that those with the best camouflage, or those that are fastest, for example, generally survive to reproduce.

So when looking naively, you could assume that the animals would be the same where environmental conditions are the same. However, this is not the case. And this is strong Evidence for evolution.
The most used example is Australia. Australia is home to the most marsupials on the planet, but other species found elsewhere in the World are missing in Australia. This indicates that evolution occurred in this place on Earth separately … and that is why, for example, kangaroos evolved only there – this is the “path” evolution took there, and it couldn’t spread elsewhere.
Pictured:
Four of the 13 finch species found on the Galápagos Archipelago, have evolved by an adaptive radiation that diversified their beak shapes to adapt them to different food sources. (Wikipedia)
Quote about Australia:
Australia has an abundance of endemic species (those found nowhere else) which is typical of islands whose isolation by expanses of water prevents species from migrating. Over time, these species diverge evolutionarily into new species that look very different from their ancestors that may exist on the mainland. The marsupials of Australia, the finches on the Galápagos, and many species on the Hawaiian Islands are all unique to their one point of origin, yet they display distant relationships to ancestral species on mainlands.
“The biological distribution of species is based on the movement of tectonic plates over a period of time” by boundless.com is licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0
Also, Africa and South America are not that different in terms of climate; for example, Africa has giraffes, while South America has llamas and sloths.
This line of Evidence is reinforced by the previous group, which shows that “basics” for now-similar yet different species on different continents evolved when everything was one supercontinent, and later, as continents drifted apart.
4. Genetic Evidence
One of the strongest pieces of Evidence for evolution is this. Genetic Evidence. What does genetic Evidence mean? Well, we humans have the technology to study gene sequences, yes?
And scientists did study them. Genetic Evidence for evolution can be found in the similarities between the genetic markup of various species. Basically, what scientists do is: they take gene samples from animals and compare how similar they are. They compare the species, and this enables them to form a tree of cousinship – similarities in those gene samples between species indicate how “related” the species are. This is what showed them, for example, that humans and chimpanzees are very closely related.
David Hillis’s 2008 Tree of Life plot is based on completely sequenced genomes.
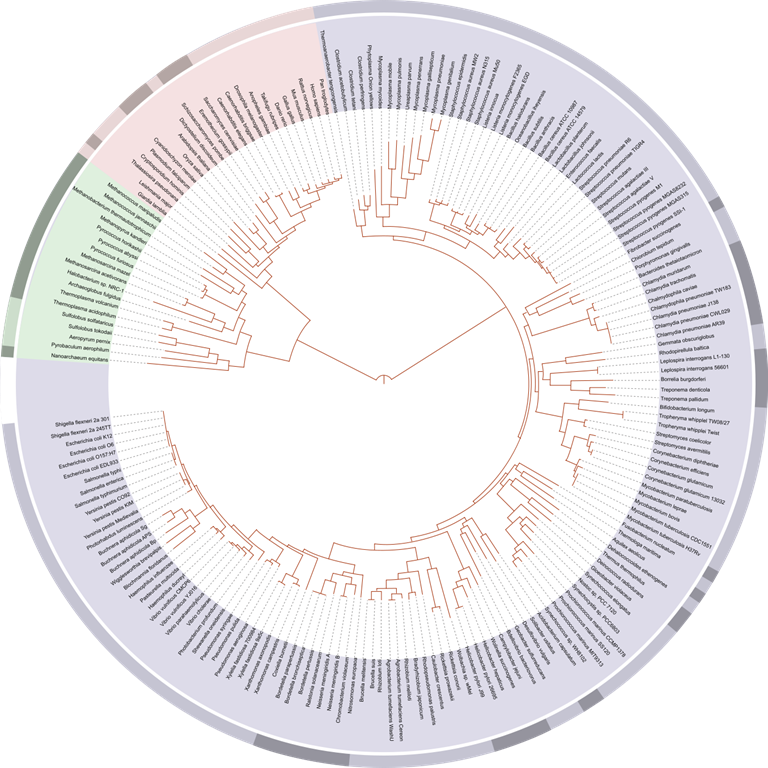
By Ivica Letunic: Iletunic. Retraced by Mariana Ruiz Villarreal: LadyofHats [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons
In short, the number of similarities shows scientists how closely related the species are. And the most beautiful thing is that the DNA evidence matches the data from previous groups. It all fits together.
5. Natural selection directly observed
Natural selection is the process by which organisms that have traits that are favourable for them to survive are more likely to reproduce and pass those traits to their offspring. This is a driving force of evolution.
When natural selection occurs and organisms with favourable traits survive to reproduce, those traits become more widely spread in the population. The new generation of animals comes from the most successful ones —the ones that survive. Others are eliminated.
Now, this process has been directly observed both in nature and in the laboratory.
Perhaps the most famous example of natural selection is the bacteria that have developed antibiotic resistance.
The concept is relatively simple, which makes you wonder how people can believe it is not true. What antibiotics do is kill bacteria, thereby applying evolutionary pressure. Now, if a genetic mutation occurs in the bacteria which enables them to survive the effects of antibiotics, these bacteria will survive in the environment. In effect, bacteria are evolving, and natural selection is directly observed.
Watch this video:
Terrifying. Let this be a lesson to you: do NOT abuse antibiotics.
Anyway, there are also other examples where natural selection is directly observed, for example, lizards that were moved to Croatian islands and evolutionary change was directly observed in their descendants:
In 1971, ten adult specimens of Podarcis sicula (the Italian wall lizard) were transported from the Croatian island of Pod Kopište to the island Pod Mrčaru (about 3.5 km to the east).
…
In the 1990s, scientists returned to Pod Mrčaru and found that the lizards currently occupying Mrčaru differ greatly from those on Kopište. While mitochondrial DNA analyses have verified that P. sicula currently on Mrčaru are genetically very similar to the Kopište source population,[209] the new Mrčaru population of P. sicula was described as having a larger average size, shorter hind limbs, lower maximal sprint speed and altered response to simulated predatory attacks compared to the original Kopište population.
(Wikipedia)
So, basically, this shows that not only the EFFECTS of evolution have been proven, but also the very mechanism of evolution has been directly observed. There really should not be any doubt: Evolution is true.
6. Additional: Evidence from mathematical modelling
Suppose scientists can use computers to simulate the amounts of dark matter in the galaxy. In that case, it only stands to reason that complex systems and processes such as evolution can be simulated as well.
A simulation has been created in which the basic concepts of evolution have been programmed into a computer. Random “mutations” were added, and the ability to preserve those that are beneficial to the simulated environment was introduced.
As the simulation was turned on, “life” reproduced and adapted to the “environment” in the same way as in “real” evolution, with beneficial traits surviving and those that were not disappearing.
You can read more about it in the “Avida” Wikipedia article, and there’s even a version for you to download and check for yourself. The source code is available on GitHub, so if you understand the details and code, you can check it for yourself.
Conclusion
If you have just a bit of time on your hands, you can examine the Evidence and discover for yourself that evolution is true and that it really happened. You do not have to be a scientist, as the Evidence is so strong that it just makes sense. So, the only things you need are free time, common sense and an open mind.




